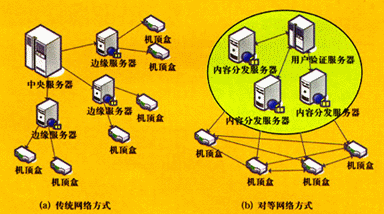
With the rapid development of embedded technology in recent years, streaming media technology that is showing strong market demand on the personal computer platform has gradually shifted to embedded platforms. The personal consumption and home appliance media consumption demand provides a market opportunity for the transfer of this platform. IPTV is at the forefront of this consumer revolution. Most of the industry believes that IPTV contains huge commercial interests, but there are still few people involved, one of the reasons is the speed of the network. This paper introduces peer-to-peer network technology, namely peer-to-peer (P2P) technology, which is applied to IPTV network transmission, which can make full use of the uplink and downlink channels of each terminal, and does not require hardware such as routers to support multicast, and can transmit for IPTV network. The bottleneck problem provides a solution. This article refers to the address: http:// First, peer-to-peer network technology 1. Introduction to peer-to-peer network A peer-to-peer network, often referred to as P2P or peer-to-peer, is a new type of network technology that has emerged in recent years. It breaks the server/client (C/S) mode of the traditional network in the transmission mode, and establishes a direct communication mechanism between the client and the client. This communication method also provides ideas for the future development of the network. In a peer-to-peer network, each node serves as both a client and a server for others. In a sense, each node is in the same position. Peer-to-peer network is a successful extension of the distributed concept. It distributes the server burden in the traditional way to each node in the network. Each node will undertake limited storage and computing tasks. The more nodes are added to the network. More, the more resources a node contributes, the higher the quality of its service. On the other hand, the C/S service model still dominates on the Internet. Although the network bandwidth of end users has increased year by year in recent years, the user experience has not changed much, mainly because the major servers are overwhelmed and the number of users is large. When it rises, the server is even in danger of collapsing, and the idle link bandwidth is being wasted. The P2P network service can just fully exploit the idle resources of the network and can serve more users without increasing investment. It can thus be seen that the advantages of peer-to-peer networking technology are self-evident, and it will create tremendous value in future network applications. 2. The basic structure of a peer-to-peer network Peer-to-peer networks are generally classified into three types according to their organizational structure. (1) Centralized peer-to-peer network A centralized peer-to-peer network is not a peer-to-peer network in a complete sense. This is an extension of the traditional network approach based on the P2P concept between the C/S model and the peer-to-peer network. The centralized peer-to-peer network is based on a central directory server, which provides directory query services for each program in the network, and the content does not need to go through the central server. This kind of network has a relatively simple structure and the burden on the central server is greatly reduced. However, since there is still a central node, it is easy to form a transmission bottleneck, and the scalability is also poor, which is not suitable for a large network. However, due to the centralized management of the directory, it is an alternative to the management and control of small networks. (2) Unstructured distributed network The most significant difference between an unstructured distributed network and a centralized one is that it does not have a central server, and all nodes access the entire network by communicating with neighboring nodes. In an unstructured network, nodes use a mechanism for querying packets to search for the resources they need. The specific method is that a node sends a query packet containing the query content to a node adjacent thereto, and the query packet spreads in the network in a diffused manner, because if the method is not controlled, the message floods, so Generally, an appropriate time to live (TTL) is set, which is decremented during the query. When the TTL value is 0, the transmission will not continue. This unstructured way, the organization is relatively loose, the nodes are relatively free to join and leave, when searching for popular content, it is easy to find, but if the content of the demand is relatively unpopular, the smaller TTL is not easy to find, but Large TTL values ​​can easily cause large query traffic. Especially when the network range is extended to a certain scale, even if the limited TTL value is small, the traffic will increase dramatically. However, when there are some so-called class server nodes with abundant resources in the network, the efficiency of the query can be significantly improved. (3) Structured distributed network Structured distributed networks are the result of research based on Distributed Hash Table technology in recent years. Its basic idea is to organize all the resources in the network into a huge table, the table contains the keywords of the resources and the address of the stored nodes, and then the table is divided and stored separately for each node in the network. Go in. When the user searches for the corresponding resource in the network, it can discover the node where the hash table content corresponding to the keyword is stored, store the node address containing the required resource in the node, and then initiate a search. Based on these address information, the node connects to the corresponding node and transmits resources. This is a technically advanced peer-to-peer network. It is highly structured and highly scalable. Nodes are free to join and leave. This approach is suitable for larger networks. Second, the application of peer-to-peer network technology in IPTV 1. Status of IPTV Domestic IPTV and P2P have been developed in two different directions. Because IPTV is similar to traditional TV viewing, it is basically regarded as an upgrade of cable television (CATV) or digital television (DVB). Therefore, a similar central server model is used in the design. In the traditional way, the network is basically a broadcast unidirectional channel, that is, the client has no ability or only has the ability to send uplink information. In this way, all service content is sent by the central server, and all processing work Completely done by the central server, P2P connections cannot be achieved. In order to solve the server bottleneck problem in IPTV in C/S mode, most of the current solutions are proposed to adopt multicast technology and the content distribution strategy (CDS) of the central server-edge server. Multicast technology is also very popular in recent years, and it is better than the one-to-multipoint transmission service technology in the broadcast mode network. In traditional point-to-multipoint communication, the server establishes an independent connection for each client that requests connection. The maximum number of connections that a typical server can provide is quite limited, so this method is not suitable for media services. In the broadcast mode, it is not necessary to establish a corresponding connection for each user, and only a content that is required is sent to each subnet in a broadcast manner, so that all users can receive the data. However, the drawbacks of this approach are obvious. A large number of users who have not requested this content have also received this data, which will cause flooding of network data and cause blocking. As a result, multicast technology has emerged. In multicast mode, the concept of a multicast group is added. When a user requests a service, the group is added. The server only sends a copy of the data to the multicast address of the subnet in need. When the data reaches the subnet. When the router is connected, the router will send according to the current group membership status, so that only the current group members can receive the data, thus ensuring that the bandwidth is not wasted. 2. Peer-to-peer network application in IPTV Multicast has a considerable effect on reducing the burden on the server. However, multicast requires high hardware, and the underlying network that needs both the data source and the receiver can support the multicast protocol. Moreover, the multicast mode still does not utilize the uplink channel of the client, that is, the data received by the user cannot be forwarded to other users who have the same needs. The network structure of the traditional network mode and the peer-to-peer network mode is shown in Figure 1. The IPTV system using peer-to-peer network technology basically has no requirements for the underlying hardware, and only needs to be modified at the application layer. Since IPTV has the characteristics of real-time media, the network node does not need to store related content of resource information, and each node can only provide one resource service at a certain time. Therefore, the search-based mechanism in the peer-to-peer network can be completely ignored. In addition, since the IPTV system must have a good user authentication charge management subsystem and the function of providing related value-added services, the user cannot be allowed to join the network casually, and a sound user management mechanism is required. For the characteristics of IPTV, it is more appropriate to apply a peer-to-peer network technology in IPTV. Figure 1 Comparison of the structure of traditional networks and peer-to-peer networks in IPTV In a centralized architecture based on peer-to-peer network IPTV systems, there should be a small number of central servers in the system. In addition to saving program content resources, these servers also store current program listing information and client information that is watching programs. When the user requests to view a certain program, the server will return to the user who is watching the program, where the server can select the closest user to the requesting user among all the users who watch the program according to the routing information of the request source, that is, the most connected. Good user information is returned. After receiving the address information returned by the server, the user starts to connect with the user who is watching, and obtains the program content. Embedded Scanner,Scanner With Laser,Bar Code Scanner,2D Stationary Barcode Scanner Guangzhou Winson Information Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.barcodescanner-2d.com