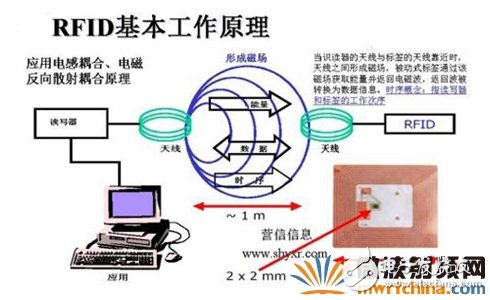
RFID readers can only read or write an RFID card in a magnetic field at normal time. However, in actual applications, there are often multiple RF cards that enter the reader's RF field at the same time. How does the reader handle? What? The reader needs to select a specific card for reading or writing. This is the tag anti-collision. The anti-collision mechanism is a unique problem in RFID technology. There is no conflict in the operation of the contact IC card, because the reader of the contact smart card has a special card holder, and only one card can be inserted in one card holder, and there is no reader and two sheets are faced at the same time. Problems with the above card. The anti-collision mechanisms in common non-contact RFID cards are mainly the following: The high-frequency ISO14443A uses this anti-collision mechanism, which is based on the fact that the card has a globally unique serial number. For example, Mifare1 card, each card has a globally unique 32-bit binary serial number. Obviously, each bit of the card number is not "1" or "0", and since it is the only one in the world, the serial number of any two cards always has a different value, ie there is always a certain bit. One card is "0" and the other card is "1". When two or more cards enter the RF field at the same time, the reader/writer sends a card call command to the RF field and asks if there are any cards in the RF field. These cards also answer "there are cards"; The reader then sends the anti-collision command "Tell me your card number". After receiving the command, all cards return their own card number. It is possible that the first few digits of these card numbers are the same. For example, if the first four digits are all 1010, there is a card in the fifth digit that is "0" and the other card is "1", so when all the cards say their fifth card number together, because the card says "0", A card says "1" and the reader has heard a conflict. After the reader detects the conflict, it tells the card in the RF field that the first four digits of the card number are "1010", and the fifth card with the "1" continues to say its own card number, and other cards do not have to speak. As a result, the card with the fifth digit "1" continues to speak. There may be more than one card with the "1" in the fifth digit. Therefore, a conflict occurs in the process of returning the card number to these cards. The reader continues to use the above method. The card with the conflict bit "1" continues to speak, and other cards are forbidden to speak. Eventually after several anti-conflict cycles, when there is only one card, there is no conflict, and the winning card returns its complete card number. To the reader/writer, the card reader issues a card selection command, this card is selected, and other cards can only participate in the anti-collision process again when they wait for the next card call. In the anti-collision process described above, when a conflict occurs, the reader/writer always selects a card having a conflict bit of “1†to win, and of course, a card having a conflict bit of “0†may be designated to win. The above process is a bit personified, how do the readers know that there is a conflict in practice? In the previous data encoding, we have already mentioned that the card sends to the reader a Manchester side code commanding the use of subcarrier modulation, the right half of the subcarrier modulation symbol represents the data "0", the subcarrier modulation The left half of the symbol represents data "1". When a collision occurs, the card will return "0" and "1", resulting in the entire symbol having subcarrier modulation. The reader receives such a symbol. You know there is a conflict. This method can guarantee that a card can be selected under any circumstances. Even if all cards of the same type in the world are used to prevent conflicts, a card can be selected after a maximum of 32 collision prevention cycles. The disadvantage is that because the card serial number is the only one in the world, and the length of the card number is fixed, the production quantity of a certain type of card is also certain. For example, a common Mifare1 card has only 4 bytes of card serial number, so its The maximum number of productions is 32, which is 4294967296. This anti-collision mechanism is used in ISO14443B. The time slot (TImeslot) here is actually a serial number. The range of this serial number is specified by the reader. Possible ranges are 1-1, 1-2, 1-4, 1-8, and 1-16. When two or more cards enter the RF field at the same time, the reader/writer sends a card call command to the radio frequency field. The command specifies the range of the time slot, and the card randomly selects a number as its own temporary identification number within the specified range. The reader then calls the number from 1 and if a number is exactly one card selected for that number, the card is selected to win. If the called number has no card answer or there is more than one card answer, continue the downward call. If all the numbers in the range are called once and a card has not yet been selected, the card is reselected to randomly select the temporary identification number until a card is called. This approach does not require the card to have a globally unique serial number, so there is no limit to the number of cards that can be produced, but in theory there is a possibility that no card will ever be selected. Felica also uses this mechanism. This mechanism is used in ISO15693. On the one hand, each card has a 7-byte globally unique serial number. On the other hand, the reader/writer uses the time slot numbering method in the anti-collision process. However, the number here is not a randomly selected card, but a card. Part of the unique serial number. The range of the calling number is 0-1 and 0-15. The general process is that when there are multiple cards entering the RF field, the reader sends an inventory request command. If the designated card number range is 0-15, the card with the lowest 4 digits of the card serial number is 0000 and sends back its own 7 words. Section number. If there is no conflict, the serial number of the card is registered in the PCD. The reader then sends an end-of-frame flag to acknowledge that the card with the lowest 4 bits of the card's sequence number is 0001. After that, the reader sends one end-of-frame flag, which means that the lowest 4 bits of the sequence number are incremented by 1 until the lowest 4 bits. Cards for 1111 are required to answer. If there is no conflict when a card returns a serial number during this process, the reader can select this card; if there is no card reaction during the inspection, it means that there is no card in the RF field; if a time slot for card reaction occurs Conflicts, such as a conflict between the card with the lowest 4 digits of the 1010 card returning card number, the reader specifies in the next anti-collision cycle only the card with the lowest 4 digits of 1010 to participate in the anti-collision, and then use the 5-8 bits of the card as the time Gap, repeat the previous inspection. If the 5-8-bit time slot of the called card is also the same, then use the 9-12 bits of the card as the time slot, repeat the previous inspection, and so on. The reader can specify the serial number of any number of bits from the lower bit, so that the card with the lowest card number and the specified lower serial number participate in the anti-collision cycle. The card uses one or four digits in front of the specified number as the time slot for the reader. The call number responds. Since the serial number of the card is globally unique, any two cards always have a certain continuous four-digit binary number, so that a card can always be selected. It should be pointed out that when the number of selected slots is 1, this anti-collision mechanism is equivalent to a bit-oriented anti-collision mechanism. RFID working principle diagram In addition, it should be noted that TTF (Tag Talk First) cards are generally unable to prevent collisions. When this type of card enters the RF field, it will automatically send its own identification number. When multiple cards enter the RF field at the same time, the card will not be read. At this time, only the holders of the cards themselves must avoid conflicts. 8 Pin Automotive Connector Housing Wenzhou Langrun Electric Co.,Ltd , https://www.langrunele.com