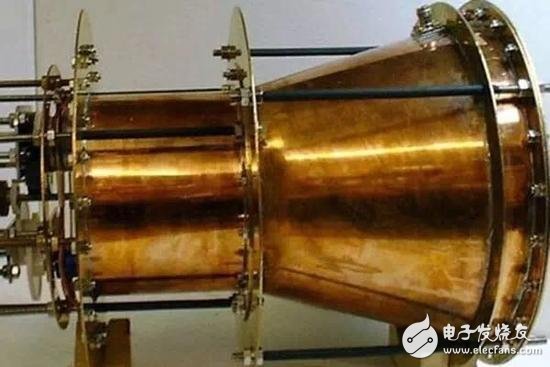
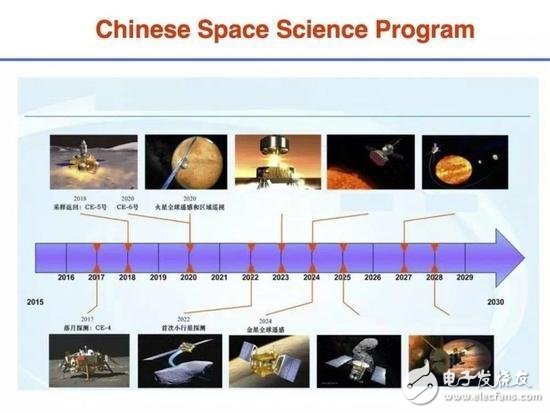
The EM engine is the abbreviation of English "ElectromagneTIc Drive", which refers to a new driving method - electromagnetic drive. The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) completed a new EM engine test and published a paper argument. However, China conducted a space test on Tiangong-2, which is currently in a leading position. The breakthrough in China's research on this research has aroused great concern from foreign media. Recently, the National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA) completed a new EM engine test and published a paper argument. The paper entitled "Measurement of Pulse Thrust from Closed RF Cavity in Vacuum" has been published in the Journal of the American Academy of Aeronautics and Astronautics (AIAA) and published in December. The paper presents a series of successful tests conducted by the NASA Eagles Laboratories. The authors say they have built a prototype of the EmDrive engine that runs smoothly. The EmDrive engine requires no fuel and it is said that it takes only 10 weeks to send humans to Mars. NASA Eagle Work Lab's EmDrive Engine The EmDrive engine was originally proposed by British researcher Roger Shawyer around 2000. The principle of the EmDrive engine is to let the photon microwaves bounce inside the closed cone, creating thrust at the thinner end of the cone and propelling the spacecraft forward. But from Newton's third law of kinematics, this is impossible, because any movement will produce equal magnitude of reaction, and the EmDrive engine will not spray any scrap. (You can think of the rockets, they are the thrust that advances by ejecting gas and other substances at high speed.) A prototype of the EmDrive engine The research team led by Harold “Sonny†White at NASA's Johnson Aviation Center did detect a weak thrust. In this latest study, the researchers tested the performance of the device in a vacuum and found that “the thrust data at forward, backward, and at rest shows that the system can produce 1.2 millinewtons per kilowatt (positive and negative fluctuations). The thrust of 0.1) is very close to the average performance of the system operating in air." White and colleagues pointed out in the paper that this thrust is more than 100 times that of the solar sail. Similar to the solar sail, the EmDrive engine does not require any propellant, and the spacecraft using the propulsion system can generate the required microwaves through solar panels. Therefore, the EmDrive engine can greatly reduce the cost of space travel, increase flight speed, and help us better explore the universe. Since 2010, China and the United States have invested enormous manpower and resources in this EM engine research. Recently, China announced that it has achieved a key breakthrough. Dr. Chen Yue, Director of the China Aerospace Technology Research Institute (CAST) Commercial Aerospace Technology Center, disclosed for the first time on December 10, 2016. China has now verified the technology of the fuel-free engine EmDrive not only in the laboratory, but also verified the principle. The test was carried out in a zero-gravity environment of the orbit. According to the International Business Times, China tested the electromagnetic drive engine at Tiangong No. 2. The Tiangong-2 Space Laboratory was successfully launched at the Jiuquan Satellite Launch Center on September 15, 2016 at 22:04:09. This is China's first real space laboratory, equipped with 14 applications such as space cold atomic clocks, equipped with on-orbit maintenance technical verification devices, mechanical arm operation terminal on-orbit maintenance test equipment and other space science and technical tests, including EM engine testing. China's deep space exploration program In the future, deep space exploration is an important plan for China's space science research, including observations of Mars, Venus, asteroids, and the Sun and Jupiter. The EM engine will make deep space exploration tasks easier to operate. Although the EM engine may be lower than the rush, it lacks gravity and friction in deep space, allowing it to accelerate to high speed in sufficient time, even starting from a low power level. The performance of the engine depends on the cavity material (to reduce the loss of EM absorbed by the cavity wall) and the temperature, which can affect the electromagnetic field, which indicates that future EM engines made of superconducting materials will have high performance specifications. Spacecraft or satellites must also be designed from the ground up to maximize the efficiency of the EM drive. It is worth noting that the EM engine may also be susceptible to the erratic radiation effects of space weather, so the proof-of-concept test of the EM engine on the Tiangong-2 is very important. The EM engines are ideal for deep space exploration because they eliminate the need for refueling and even the weight and space required to store fuel, simplifying logistics and design. In theory, all spacecraft require an EM engine as a source of energy, like solar energy or reactors, to provide energy from the Mars mission to the robotic detector beyond the solar system. The use of the EM engine will also make the satellites smaller and more efficient, as they may not require a chemical propeller for maneuvering space consumption. The application of such a system (if it actually proves to be viable) is a lot. If China can install EM engines on its satellites for orbital maneuvers and height control, they will become cheaper and more durable. Li Feng, a commercial satellite designer at the China Academy of Space Sciences, said that the current EM engine has only one kilogram of thrust for orbit adjustment; medium-sized satellites require 0.1-1 Newton. The functional EM engine will also open up new possibilities for long-range Chinese interstellar detectors outside the asteroid belt, while releasing the mass of fuel in the manned spacecraft for other supplies and equipment to build the moon. And the Mars base. On the military side, the EM engine can also be used to create more secretive, longer-lasting Chinese surveillance satellites. 48V15Ah Lithium Ion Battery,48V15Ah Lithium Battery Pack,Li-Ion 48V15Ah Lithium Battery Pack,Echargeable Lithium Battery Pack 48V Jiangsu Zhitai New Energy Technology Co.,Ltd , https://www.zttall.com