The nonlinear distortion of the RF power amplifier will cause it to generate new frequency components, such as second harmonics and double-tone beat frequencies for second-order distortion, and third harmonics and multi-tone beat frequencies for third-order distortion. If these new frequency components fall within the passband, they will cause direct interference to the transmitted signal. If they fall outside the passband, they will interfere with the signals of other channels. To this end, the RF power amplifier should be linearized, which can better solve the problem of signal spectrum regeneration. The principle and method of the basic linearization technology of the RF power amplifier is nothing more than taking the amplitude and phase of the envelope of the input RF signal as a reference, comparing it with the output signal, and then generating an appropriate correction. There are three common techniques for linearizing RF power amplifiers: power backoff, predistortion, and feedforward. Follow WeChat Download Audiophile APP Follow the audiophile class related suggestion NXP Semiconductors NV (NASDAQ: NXPI) today launched a full range of super ... Radio frequency power monitoring circuit, radio frequency entry point, monitoring point, radio frequency power monitoring circuit.
1. Power back-off This is the most commonly used method, which is to select a tube with a larger power as a small power tube. In fact, it sacrifices DC power consumption to improve the linearity of the power amplifier.
The power back-off method is to reduce the input power of the power amplifier from the 1dB compression point (the amplifier has a linear dynamic range, within this range, the output power of the amplifier increases linearly with the input power. As the input power continues to increase, the amplifier gradually enters In the saturation region, the power gain begins to decline. The output power value when the gain is reduced to 1dB lower than the linear gain is usually defined as the 1dB compression point of the output power, expressed as P1dB.) Backward 6-10 dB, working at a far distance At the level of less than 1dB compression point, the power amplifier is away from the saturation region and enters the linear working region, thereby improving the third-order intermodulation coefficient of the power amplifier. In general, when the fundamental power is reduced by 1dB, the third-order intermodulation distortion is improved by 2dB.
The power back-off method is simple and easy to implement, does not require any additional equipment, is an effective method to improve the linearity of the amplifier, the disadvantage is that the efficiency is greatly reduced. In addition, when the power backs up to a certain degree, when the third-order intermodulation reaches -50dBc or less, continuing to back off will no longer improve the linearity of the amplifier. Therefore, it is not enough to rely solely on power back-off in occasions with high linearity requirements.
2. Pre-distortion Pre-distortion is to add a nonlinear circuit in front of the power amplifier to compensate the nonlinear distortion of the power amplifier.
The advantage of predistortion linearization technology is that it does not have stability problems, has a wider signal frequency band, and can handle signals with multiple carriers. The cost of predistortion technology is low. It consists of several carefully selected components packaged into a single module and connected between the signal source and the power amplifier to form a predistortion linear power amplifier. The power amplifier in the handheld mobile station has adopted predistortion technology, which reduces the intermodulation products by a few dB with only a few components, but it is a critical few dB.
Predistortion technology is divided into two basic types of RF predistortion and digital baseband predistortion. RF predistortion is generally implemented by analog circuits, which has the advantages of simple circuit structure, low cost, easy high-frequency, broadband applications, etc. The disadvantage is that there is less improvement in spectral regeneration components, and it is more difficult to cancel higher-order spectral components.
Digital baseband predistortion can be realized by digital circuits because of its low operating frequency, and it has strong adaptability. It can also be used to increase the sampling frequency and increase the quantization order to offset the higher-order intermodulation distortion, which is a promising method. . This predistorter consists of a vector gain adjuster, which controls the amplitude and phase of the input signal according to the contents of a look-up table (LUT). The amount of predistortion is controlled by the input of the look-up table. Once the vector gain regulator is optimized, it will provide a nonlinear characteristic opposite to the power amplifier. Ideally, the intermodulation products output at this time should be equal to the output amplitude of the two-tone signal through the power amplifier and opposite in phase, that is, the adaptive adjustment module is to adjust the input of the lookup table, so that the difference between the input signal and the output signal of the power amplifier is minimized . Note that the envelope of the input signal is also an input to the look-up table. The feedback path samples the distorted output of the power amplifier and then sends it to the adaptive DSP through A / D conversion to update the look-up table.
3. Feed-forward The feed-forward technology originated from "feedback". It should be said that it is not a new technology. It was proposed by Bell Labs in the US in the 1920s and 1930s. In addition to the calibration (feedback) is added to the output, the concept is completely "feedback."
Feedforward linear amplifiers form two loops through couplers, attenuators, synthesizers, delay lines, and power dividers. After the RF signal is input, it is divided into two channels by a power divider. All the way into the main power amplifier, due to its nonlinear distortion, in addition to the main frequency signal that needs to be amplified at the output, there is also third-order intermodulation interference. A part of the signal is coupled from the output of the main power amplifier, and the main carrier frequency signal of the amplifier is cancelled through the loop 1, so that only the inverted third-order intermodulation component remains. After the third-order intermodulation component is amplified by the auxiliary amplifier, the intermodulation component generated by the non-linearity of the main amplifier is canceled through the loop 2, thereby improving the linearity of the power amplifier.
The feed-forward technology provides both the advantages of higher calibration accuracy and the disadvantages of instability and limited bandwidth. Of course, these advantages come at a high cost. Due to the high power level in the output calibration, the calibration signal needs to be amplified to a higher power level, which requires an additional auxiliary amplifier, and requires the auxiliary amplifier itself. The distortion characteristics should be above the specifications of the feedforward system.
The cancellation requirements of the feedforward power amplifier are very high, and it is necessary to obtain the matching of the amplitude, phase and delay. If there is power change, temperature change and aging of the device, it will cause the offset to disappear. To this end, adaptive cancellation techniques are considered in the system so that the cancellation can keep up with changes in the internal and external environment. 



Interesting and informative information and technical dry goods
Create your own personal electronic circle
Lock the latest course activities and technical live broadcast
comment
Publish
NXP launches overmolded plastic (OMP) RF power devices
Posted at 2011-06-24 10:48 • 852 times read
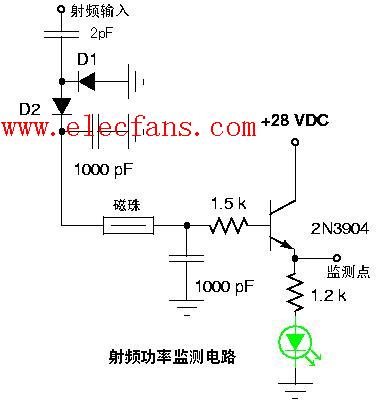
RF power monitoring circuit
Posted at 2010-05-13 18:23 • 363 views