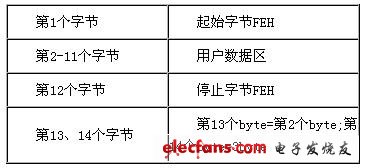
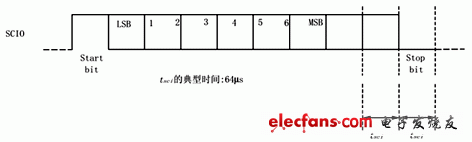
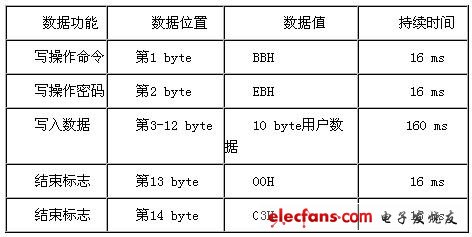
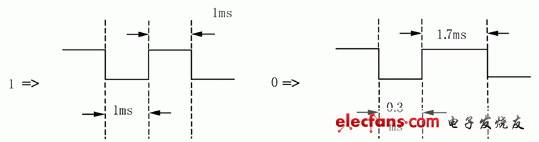
0 Preface Radio frequency identification (ie RadioFrequencyIdenTIficaTIon, hereinafter referred to as RFID) technology is an automatic identification technology that emerged from the 1990s. It uses wireless radio frequency for contactless two-way communication to achieve identification purposes and exchange data. Different from the contact recognition technology such as magnetic card and IC card, the RFID tag can be recognized without physical contact between the electronic tag and the reader, so it can realize multi-target recognition and moving target recognition, and can be used in a wider range of occasions. application. The radio frequency identification system developed in this paper and the corresponding data verification algorithm are a successful attempt of radio frequency identification technology. 1 Principle of radio frequency identification A typical RFID system consists of an electronic tag (Tag), a reader/writer (Read/Write Device), and a data exchange and management system. Electronic tags, also known as RF cards, have the ability to intelligently read and write and encrypt communications. The reader is composed of a wireless transceiver module, an antenna, a control module, and an interface circuit. Radio frequency identification is a passive system, that is, the electronic tag does not contain a battery, and the energy of the electronic tag is provided by the radio frequency pulse emitted by the reader. The electronic tag receives the RF pulse, rectifies and charges the capacitor. The capacitor voltage is regulated and used as the operating voltage. The data demodulation section demodulates the data from the received RF pulses and sends them to the control logic. Control logic accepts instructions to complete storage, send data, or other operations. The EEPROM is used to store the ID number of the electronic tag and other user data. 2 RFID system design At present, major chip manufacturers have developed ASICs (digital analog logic hybrid dedicated circuits) for radio frequency identification. The radio frequency identification system developed in this paper is based on Texas Instruments' TMS3705 base station chip, and the base station chip design base station transmitting and receiving circuits. Design the base station antenna at the same time. Based on the TMS3705 base station chip to build a radio base station, Taiwan Lianyang Electronics provided a radio base station module RFM001 based on TMS3705. Figure 1 Base station chip and radio base station module After the RF card transmits the data, it is received by the RF base station antenna. After being processed by the base station, the data stream obtained by the output pin of the base station is sent to the input port of the microprocessor. The base station only performs signal reception and rectification work, and the demodulation and decoding of the signal is performed by the microprocessor. The microprocessor should perform the decoding operation according to the analog signal at the high level and the low level for the analog timing. The more popular coding methods are Mancheester coding and Biphase coding. The system is based on the TMS3705 base station chip radio frequency identification system. The radio frequency card used is the RFM001 read/write card. To correctly complete the development of the radio frequency identification system, it is necessary to understand the read and write characteristics of the used radio frequency card. These features include: EEPROM memory allocation, card synchronization signals, transmit frequency, card control logic, write card and other card operation command formats. 2.1 Data Storage Format in RFM001 RF Card Contains 14 bytes of data for Startbyte The user data area has a total of 10 bytes. It is recommended to perform CRC check on the data. Therefore, it is recommended that the 2-9 byte be the user data area, and the 10th and 11th bytes be the CRC check code. The timing of reading data by the base station (see Figure 2) is given below, and the data sent by the RF card is modulated by FSK. Figure 31 byte transfer format The format of each Byte is shown in Figure 3. It consists of 10 bits. The first bit is the STARTbit fixed to HI, the last bit is the Stopbit fixed to LOW, and the 2-9bit actually sends the data (the first received bit is LSB) Because it is negative logic data, it needs to be inverted (LOW=1, HI=0). 2.2 RFM001 RF Card Write Format To write user data to an RFM001 RF card, the following format must be followed. The data in the user data area can be completely determined by the user, but it is recommended to use the CRC check of the 2 byte check code to verify the data. Therefore, for 10 bytes of user data, the first 8 bytes are used as user data, and the last 2 bytes are used as CRC check codes for user data. For one-bit write, pulse width modulation is used. It is determined whether to write 1 or write 0 according to the difference of duty ratio. The specific duty ratio is shown in Figure 4. Figure 4 bit write mode
Immersion Cooling is a technique used to cool components of IT equipment that consists of submerging the computer components in a thermally conductive and dielectric liquid. Through this practice, the servers are cooled and heat is transferred from the source to the liquid.
water cooling,oil cooling,immersion cooling box,liquid immersion cooling,apw12 power supply Shenzhen YLHM Technology Co., Ltd. , https://www.nbapgelectrical.com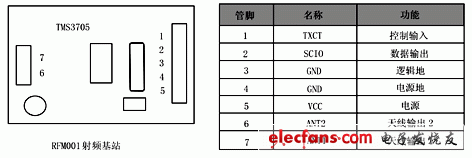
When we talk about Immersion Cooling, we also need to discuss the different types of Immersion Cooling, as well as the applications of Immersion cooling. The practice of Immersion Cooling has a multitude of benefits particularly as it allows datacenters to be managed in a greener and more sustainable manner. Environmental concerns has been a huge catalyst for the adoption of the technology in recent years.
deionized water
mineral oil
fluorocarbon-based fluids
synthetic
Immersion Cooling systems used to have a higher fluid cost than water cooling, but this is already changing.
A wide variety of liquids exist for this purpose, the most suitable being transformer oils and other electrical cooling oils. Non-purpose oils, including cooking, motor and silicone oils, have been successfully used for cooling personal computers