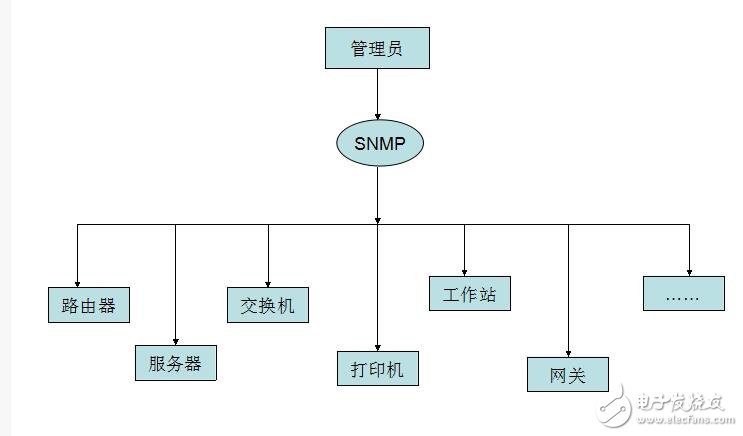
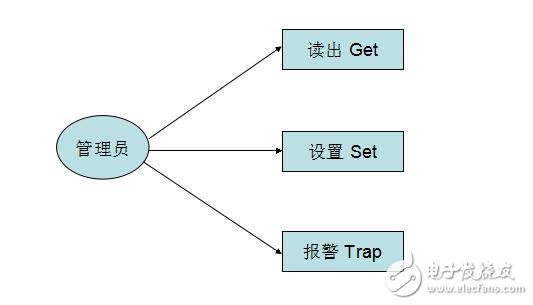
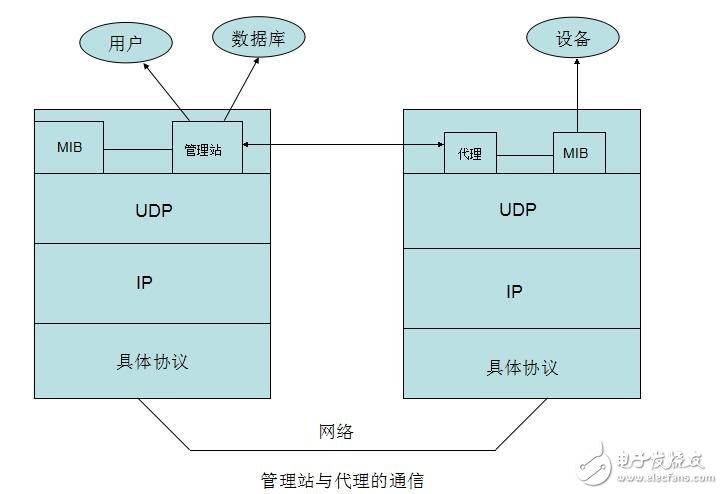
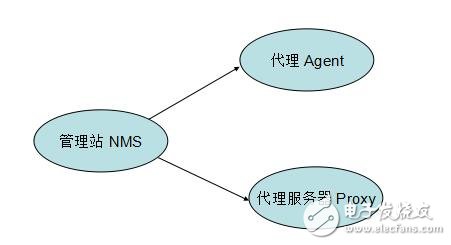
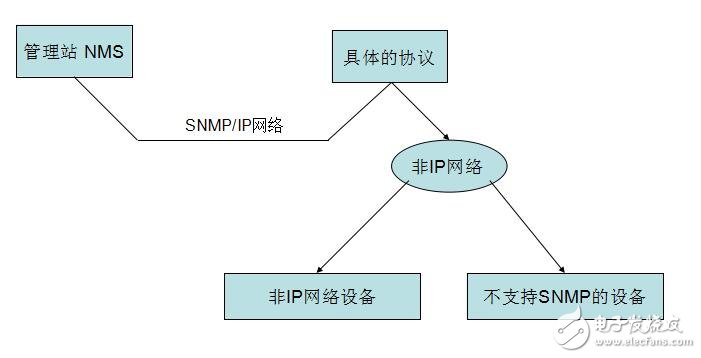
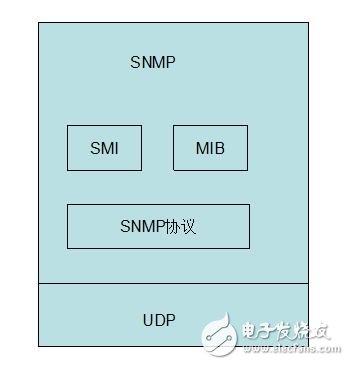
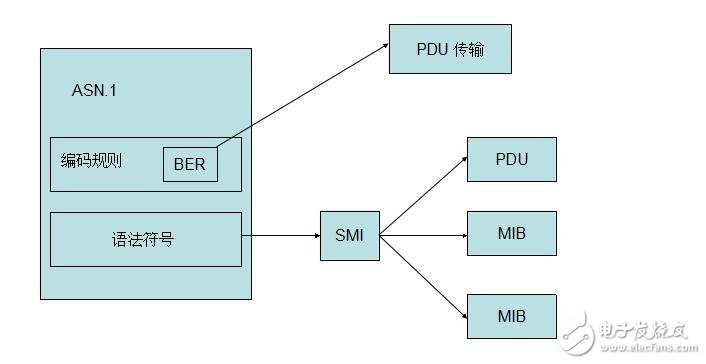
Simple Network Management Protocol (SNMP) consists of a set of network-managed standards, including an application layer protocol (applicaTIon layer protocol), a database schema, and a set of resource objects. The protocol can support a network management system to monitor whether devices connected to the network have any management concerns. The agreement is part of the internet protocol suite defined by the Internet Engineering Task Force (IETF). The goal of SNMP is to manage the software and hardware platforms produced by many manufacturers on the Internet. Therefore, SNMP is greatly affected by the Internet standard network management framework. SNMP has come out to the third version of the protocol, and its functionality has been greatly enhanced and improved. The role of SNMP SNMP is the most commonly used network management protocol since 1990. SNMP is designed to be protocol-independent, so it can be used on IP, IPX, AppleTalk, OSI, and other transport protocols used. SNMP is a set of protocol suites and specifications (see table below) that provide a way to collect network management information from devices on the network. SNMP also provides a way for devices to report problems and errors to network management workstations. Now, almost all network equipment manufacturers have implemented SNMP support. Trending SNMP is a public communication protocol that collects management information from devices on the network. The device manager collects this information and records it in the Management Information Base (MIB). This information reports device characteristics, data throughput, communication overloads, and errors. The MIB has a common format, so SNMP management tools from multiple vendors can collect MIB information and present it to the system administrator on the management console. By embedding SNMP into a data communication device, such as a router, switch, or hub, you can manage these devices from a central station and view the information graphically. Many of the management applications available today are typically run under most currently used operating systems, such as Windows 95, Windows 98, Windows NT, and different versions of UNIX. A managed device has a management agent that is responsible for requesting information and actions from the management station. The agent can also actively provide information to the management station by means of traps. Therefore, some key network devices (such as hubs, routers, switches, etc.) provide This management agent, also known as an SNMP agent, is managed through an SNMP management station. The basic idea of ​​SNMP: Defined as a unified interface and protocol for different types of devices, devices produced by different manufacturers, and devices of different models, so that administrators can manage these network devices that need to be managed with a uniform appearance. . Through the network, administrators can manage devices located in different physical spaces, which greatly improves the efficiency of network management and simplifies the work of network administrators. SNMP is designed to work on the TCP/IP protocol suite. SNMP works on the TCP/IP protocol to manage devices that support SNMP in the network. All SNMP-capable devices provide a unified interface to SNMP, allowing administrators to manage with a unified operation, regardless of the type of device and which manufacturer. As shown below, Fourth, SNMP-supported network management operations For network management, the data we are facing is the configuration, parameters, status and other information of the device. The operation is to read and set. At the same time, because there are many network devices, in order to get the important state of the device in time, the device can also be required. Actively reporting important status, this is the alarm function. As shown below, 1) Get: Read the status information of the network device. 2) Set: Remotely configure device parameters. 3) Trap: The management station obtains important information of the device in time. Five, SNMP implementation structure In terms of implementation, SNMP provides administrators with a network management platform (NMS), also known as a management station, responsible for the issuance of network management commands, data storage, and data analysis. An SNMP agent (Agent) is run on the supervised device, and the agent implements SNMP communication between the device and the management station. As shown below, The management station and the agent end interface through the MIB, and the MIB defines the managed objects in the device. Both the management station and the agent implement the corresponding MIB object, so that both parties can identify each other's data and implement communication. The management station applies to the agent for the data defined in the MIB, and after the agent recognizes, converts the data related to the status or parameters provided by the management device into a format defined by the MIB, and responds to the management station to complete a management operation. Existing devices can be network supported by adding an SNMP module. Older devices with expansion slots can support network management by simply plugging in an SNMP module card. Many devices, routers, and switches on the network can add network management functions by adding an SNMP network management module. The server can be implemented by running a network management process. Other service-level products can also be managed by the network management module. For example, Oracle and WebLogic have SNMP processes. After running, these system-level services can be managed through the management station. According to the different responsibilities of managers and managed devices in network management operations, SNMP defines three roles. As shown below, Network management system: also known as management station, NMS. It is the console of the system, providing the administrator with an interface to obtain and change the configuration, information, status, operation and other information of the device. The management station communicates with the Agent, performs the corresponding Set and Get operations, and receives an alert (Trap) sent by the agent. Agent: Agent is the agent of network management, responsible for the transmission of SNMP operations of management stations and devices. Between the management station and the device, communicating with the management station and correspondingly managing the request of the station, obtaining corresponding data from the device, or correspondingly setting the device to respond to the request of the management station. The agent also needs to have the ability to send reports to the management station using the Trap defined in the MIB based on the corresponding state of the device. Proxy server: Proxy is a special proxy. In places where the SNMP protocol cannot be directly used, such as heterogeneous networks and different versions of SNMP agents, Proxy replaces related devices to provide a look to the management station. Implementation. Proxy does the conversion of heterogeneous networks or different versions of proxies and corresponding SNMP data requests. As shown below, Attachment: Management Information Base MIB: defines the management information that can be used on the device. The agent and management station use the MIB as a unified data interface to communicate. Sixth, the technical content of SNMP As shown below, 1989 ------ SNMPv1 1991 ------ RMON (Remote Network Monitoring), which extends the capabilities of SNMP, including management of the LAN and management of devices attached to these networks. RMON did not modify and add SNMPv1, but only increased the ability of SNMP to monitor subnets. 1993 ------ SNMPv2 (upgraded version of SNMPv1) 1995 ------ SNMPv2 official version, which specifies how to use SNMP in OSI-based networks 1995 ------ RMON expands to RMON2 1998 ------ SNMPv3, a series of documents defines the security of SNMP, and defines the overall structure of future improvements, SNMPv3 can be used with SNMPv2, SNMPv1. SNMP: The Simple Network Management Protocol is a standard protocol for managing devices on IP-based networks. MIB: Management InformaTIon Base, which defines all parameters that can be queried and modified in the agent process. SMI: Structure of Management InformaTIon (SMS), which defines the ASN.1 type and syntax used in SNMP, and defines the types, macros, symbols, etc. used in SNMP. SMI is used for the description of subsequent protocols and the definition of MIB. Each version of SNMP may define its own SMI. ASN.1: Abstract Syntax NotaTIon One (abstract syntax definition). The official language used to define the grammar, which defines the format of the SNMP protocol data unit PDU and the management object MIB in SNMP. SNMP uses only a subset of ASN.1, and uses the language features of ASN.1 to define some custom types and type macros that make up the SMI. PDU: Protocol Data Unit, which is a packet transmitted in the network. Each SNMP operation physically corresponds to a PDU. NMS: Network Management System, also known as Network Management Station, referred to as “Management Stationâ€. It is the master controller of SNMP, provides a unified user interface to access SNMP-enabled devices, generally provides a UI interface, and has statistics, analysis and other functions, is the total console of the network management system. NMS is the initiator of network management operations. Agent: is an SNMP access agent, referred to as "proxy", which provides SNMP capability for the device and is responsible for communication between the device and the NMS. Proxy: A proxy server that performs protocol conversion on devices that implement different protocols, so that non-IP devices can be managed. Trap: is the alarm data actively sent by the device to indicate important status changes. BER: Basic Encoding Rule, basic encoding specification. Describes how to encode the value of the ASN.1 type as a string. It is part of the ASN.1 standard. BER coding divides the data into three parts of TLV, T is the abbreviation of Tag, which is the type identifier; L is the abbreviation of Length, the length of the identification type; V is the abbreviation of Value, which identifies the data content. The data is encoded in the order of the TLVs to generate a byte stream. SNMP uses the BER to encode the SNMP operation request and response and then transmit it to the receiver for decoding. 1, SNMP has several versions SNMP has three versions: v1, v2, and v3: Both v1 and v2 have basic read and write MIB capabilities. V2 adds alerts, bulk data acquisition, management station and management station communication capabilities. V3 adds USM to v2, using encrypted data and user authentication technology to improve security. In addition, RMON is an important extension of SNMP, adding subnet traffic, statistics, and analysis capabilities for SNMP. There are two versions: Rmon: Provides network layer and data link layer monitoring capabilities in the OSI seven-layer network structure. Rmon2: Provides monitoring capabilities for layers above the network layer in the OSI seven-layer network architecture. 2. Relationship between ASN.1, BER, SMI, MIB, and PDU ASN.1: Advanced data description language. Describe the type, structure, organization, and encoding method of the data. It includes two parts: symbol and grammar. SNMP uses ASN.1 to describe the PDU and the Management Object Information Base MIB. BER: Basic coding rules for ASN.1. Describe how a particular ASN.1 object is encoded as a bitstream for transmission over the network. SNMP uses BER as the coding scheme. The data is first BER encoded and then sent to the receiver via the transport layer protocol (one side is UDP). After receiving the PDU on the SNMP port, the receiver obtains specific SNMP operation data after BER decoding. SMI: is a description method of SNMP. The use of ASN.1 subtypes and symbols is specified. ASN.1 is powerful, but SNMP only uses a small part of it. For the description of this part, the scope is limited, which is SMI. SMI specifies the ASN.1 type, macro, symbol, etc. used. SMI is a subset and superset of ASN.1. MIB: is the management information base used in SNMP. The data format, type, order, meaning, etc. are defined. The object is described using the type defined in SMI and the basic type in ASN.1. It is a management information library described by SMI. Each type of event of interest has a set of MIBs. For example, the network interface has a MIB tree, TCP has a MIB tree, and UDP also has a MIB tree. PDU: is the protocol data unit of SNMP. The PDU is the basic communication format, described using ASN.1, using BER encoding, and transmitted over the transport layer protocol. 3, more standardized SNMP background SNMP is widely used as a transition technology with its easy-to-use features, and the network products used provide support for SNMP. SNMP also extends RMON with remote management capabilities, allowing administrators to manage entire subnets instead of managing devices across the entire subnet.
The LED Indicator is a device that monitors the operation or position of an electrical device with light. The indicator light is usually used to reflect the working state of the circuit (with or without electricity), the operating state (running, outage or test) of the electrical equipment, and the position status (closed or disconnected).
In our company,mainly have eight series(as follow):
AD22-22DS LED Indicator
LED Indicators,LED Indicator Light,LED Indicator Lamp,LED Indicator Bulbs Ningbo Bond Industrial Electric Co., Ltd. , https://www.bondelectro.com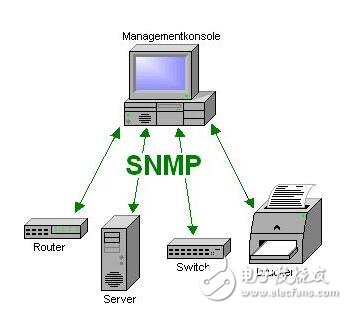
AD16 LED Indicator
AD22-22MSD Buzzer
AD22-30DS LED Indicator
AD22-DAV Current Voltage Indicator
AD22-DAM Current Indicator
AD22-DVM Voltage Indicator
First, what is SNMP