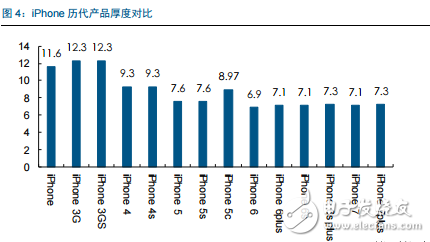
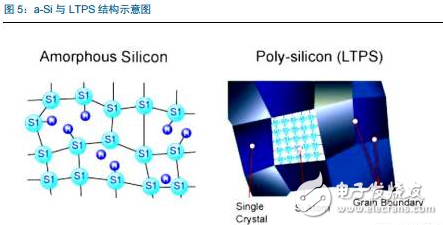
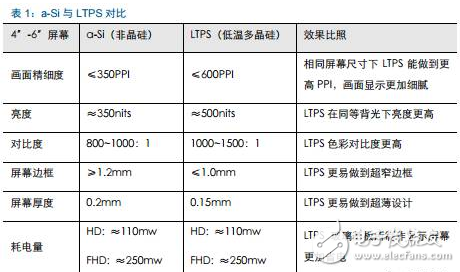
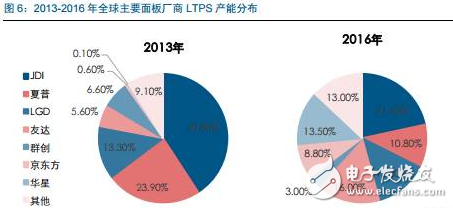
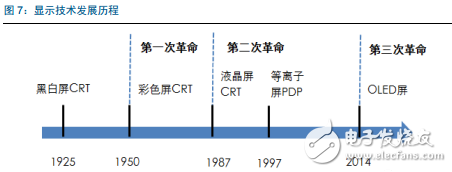
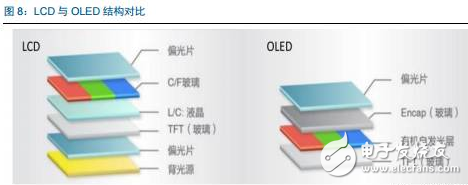
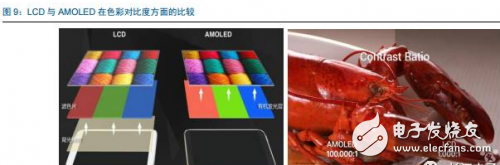
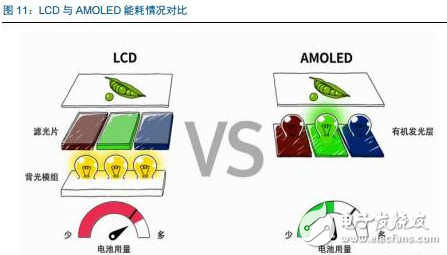
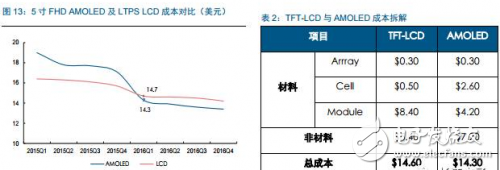
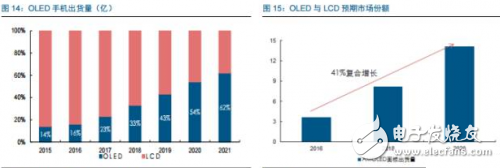
Tianma's 6th generation LTPS AMOLED production line successfully landed On April 20th, the highly anticipated Pegasus GTPS AMOLED production line (G6 LTPS AMOLED) successfully illuminates rigid and flexible AMOLED products in Wuhan, marking the success of the Tianma G6LTPS AMOLED production line. The 6th generation AMOLED production line is also the world's first 6th generation AMOLED production line that simultaneously illuminates rigid and flexible displays. The Tianma G6 LTPS AMOLED production line can not only produce advanced LTPS substrates, but also complete core processing capabilities such as OLED evaporation and packaging. It can support the production of rigid AMOLEDs, flexible AMOLEDs and flexible touch screens. It can be used for smartphones and tablets. Such as mobile smart terminal products, VR, AR and other emerging market products, as well as smart wearable, foldable devices, etc. to provide high-quality AMOLED flat and curved displays. As early as 2010, the company invested in the first 4.5-generation AMOLED pilot line in Shanghai. After several years of exploration and accumulation, the company successfully mastered the core technologies and processes. In 2013, relying on the experience of the G4.5 AMOLED pilot line, Tianma once again built a 5.5th generation AMOLED production line, which has been mass-produced and shipped to mobile smart terminal brand customers in 2016. In January 2016, the company started the construction of G6LTPS AMOLED, and realized the pre-cap of the main plant structure with the fastest construction speed in the industry, and refreshed the world's fastest lighting speed record of the same scale production line. LTPS+AMOLED will become the dual engine for driving high-end display applications Accelerated upgrade of intelligent terminals, giving rise to opportunities in the panel industry With the rapid update of the technology level, the focus of the intelligent terminal users on the product is no longer a single product performance improvement, but more attention to the aesthetics of the product design. As far as mobile phone products are concerned, thinning is the mainstream trend of product upgrades. At the same time, consumers also pay great attention to the display effect and power consumption level of the screen, which are closely related to the display technology of the screen. Therefore, the accelerated upgrade of smart terminals will further catalyze the transformation of the display panel industry. At this stage, there are two main trends in the display panel: first, the panel material is from a-Si to LTPS; second, the display technology is from LCD to AMOLED. a-Si→LTPS: main technical path for display panel material upgrade LTPS (Low Temperature Poly-silicon) is a low-temperature polysilicon technology. It was originally developed by Japanese and North American technology companies to reduce the energy consumption of Note-PC display and make Note-PC appear thinner and lighter. In the mid-1980s, the trial phase began. LTPS glass substrate manufacturing principle: using excimer laser as a heat source, after the projection system, a laser beam with uniform energy distribution is generated, which is projected onto the glass substrate of the amorphous silicon structure, and the amorphous silicon structure glass substrate absorbs the energy of the excimer laser. After that, it will be transformed into a polysilicon structure, and the entire process is completed below 600 ° C, so generally glass substrates are applicable. Compared with the conventional amorphous silicon (a-Si), the poly-Si (Poly-Si) arrangement is more tidy and directional, so the electron mobility is 200 to 300 times faster than the disordered amorphous silicon. Therefore, the display panel made of the LTPS glass substrate has advantages in resolution, response speed, brightness, etc., and the LTPS glass substrate can be used on the substrate which is simultaneously fabricated by the driving circuit to achieve system integration, thereby saving product space and driving. IC cost. Previously, Japanese manufacturers accounted for half of the LTPS glass substrate market. However, after entering 2016, a number of LTPS production lines in mainland China have entered the production line, including the 6th generation LTPS production line of Huaxing Optoelectronics and the 6th generation LTPS production line of Xiamen Tianma. At present, based on material characteristics and relatively mature processes, LTPS technology has surpassed TFT backplane driving technologies such as a-Si and IGZO, and will become the mainstream backplane driving technology of AMOLED, which has played a leading role in the evolution of display technology. LCD→OLED: the leading edge of the next generation of display technology revolution OLED (Organic Light-EmitTIngDiode) is an organic light-emitting diode technology, which was discovered in the laboratory by Chinese-American professor Deng Qingyun in 1979. Depending on the driving method, OLEDs can be classified into passive matrix (PMOLED) and active (AcTIve Matrix, AMOLED). At present, OLED display technology is praised as the third generation display technology after CRT and LCD due to its self-illumination, wide viewing angle, infinite high contrast, low power consumption and high reaction speed. It is the leading change in display technology. pioneer. From the perspective of the principle of light emission, the TFT-LCD controls the direction of rotation of the liquid crystal molecules by changing the signal and voltage on the thin film transistor (TFT), thereby achieving the purpose of controlling the polarization of each pixel to be emitted or not. Since the liquid crystal material itself does not emit light, the TFT-LCD is a passive light-emitting type display and requires backlight support. In contrast, the OLED's internal light-emitting component is an organic light-emitting diode, and different colors of light can be emitted by controlling the brightness of the red, green, and blue OLED sub-pixels, so that no external backlight is required in the AMOLED panel. AMOLED has a nearly infinite contrast. Since the backlight layer of the TFT-LCD cannot be completely turned off, the presence of light leakage causes the contrast of the picture to be lowered. AMOLED adopts active illumination mode, which can completely turn off the organic light-emitting element when no current flows, thus achieving ultra-high contrast. According to the measured data, the AMOLED screen contrast can reach 13000000:1, the bright color is more flexible when displaying the picture, and the black is deeper. AMOLED has a broader color gamut performance. The gamut range refers to the types of colors that the screen can display. The industry standard includes NTSC gamut values, sRGB gamut values, and Adobe RGB gamut values. Since the TFT-LCD performs color display by backlight filtering, the color gamut performance of the TFT-LCD is completely dependent on the spectral range of the backlight. The organic light-emitting material of AMOLED has self-luminous characteristics, and does not require a backlight module and a color filter, and has an advantage in color display. For example, the display screen of the iPhone can achieve 96% sRGB color gamut value, and the AMOLED screen used by Samsung shows that the color gamut range is close to 100% NTSC, which has exceeded the sRGB category. Therefore, the display screen of the AMOLED screen is more colorful, the level is richer, and the details are more detailed. AMOLED has a lower power consumption level. Due to the self-luminous characteristics of the AMOLED, only the necessary pixels are illuminated when the screen is displayed, and the entire backlight module is illuminated when the TFT-LCD screen is lit. At the same time, the light generated by the organic light-emitting material of the AMOLED does not need to pass through the filter, which can reduce unnecessary brightness attenuation. Therefore, AMOLED screens can save nearly 30% of energy consumption compared to TFT-LCD screens. In today's era of large-screen mobile phones, the reduction of screen power consumption becomes more important. AMOLED has a more diverse application scenario. Unlike the liquid crystal material inside the TFT-LCD panel, which is between solid and liquid, the AMOLED luminescent material exists in a solid state. Therefore, replacing the glass substrate in the display panel with a flexible plastic substrate can realize the design of the flexible display. In the future, AMOLED displays can be widely used in mobile smart terminal products such as smart phones, emerging market products such as VR and AR, as well as smart wearable and foldable devices. The advantages of AMOLED are highlighted, and the demand supply is increased. Demand side: Breaking through life and price bottlenecks, market penetration is expected to continue to increase Although AMOLED is called "fantasy display technology", its panel makers are discouraged by the short life of internal organic luminescent materials and low production yield. In 2015, with the rapid development of production technology, problems such as short service life, low production efficiency, and high investment cost hindered the development of AMOLED. The production yield of AMOLED has been greatly improved, and the production cost has been significantly reduced. The cost of AMOLED panels has been significantly reduced, and the advantages of mass production have emerged. According to IHS data, in the first quarter of 2015, the cost of a single 5-inch AMOLED panel was $19, which was 15.9% higher than the LCD cost of the same period. However, by the first quarter of 2016, the cost of AMOLED panels had dropped to $14.3, which was lower than that of the LCD panel. $14.7. At present, AMOLED panels already have the advantage of mass production cost in the low-size field. The AMOLED market penetration rate will increase, and it is expected to surpass LCD as the mainstream in 2020. AMOLED's superior product performance and increasingly lower price costs make it quickly enter the fast lane of development. In the third quarter of 2016, AMOLED panel shipments reached 96 million units, an increase of 148% year-on-year and a 103% quarter-on-quarter increase. According to UBI Research's forecast data, the demand for AMOLED in the market will continue to expand. Especially in the field of smart phones, AMOLED penetration is expected to grow from 16% in 2016 to 62% in 2021, and for the first time in 2020 beyond LCD. In terms of quantity, AMOLED panels for smartphones will grow from 358 million in 2016 to 1.408 billion in 2020, and quickly squeeze the LCD market at a compound annual growth rate of 41%. Supply side: the investment layout accelerates, and the production ramp is completed soon. The existing production line of the Korean factory is full, and the market share still dominates the world. In the field of AMOLED display panels, Samsung Display and LG almost dominate the world. Samsung Display has a 5.5-generation line with a monthly capacity of 8,000 substrates and a 6-generation line with a capacity of 15,000 substrates per month. Its market share is over 90%. In the first quarter of 2016, Samsung Display shipped 83.55 million AMOLED panels, 98 million shipments in the second quarter, and 99.7 million wafers in the third quarter. LG's small and medium-sized AMOLED panels are mainly contributed by its 4.5 generation line, with a monthly capacity of 14,000 pieces, accounting for about 8% of the market. Samsung Display and LG's AMOLED panels are mainly used for their own mobile phones, wearable devices and other products, while Samsung also signed an order with Apple for 70 million to 92 million small-size AMOLED panels, so the remaining downstream terminal manufacturers in the AMOLED panel supply. Still stretched. Samsung and LG continue to lead the investment, and other foreign major manufacturers have built factories to expand production. With the continuous expansion of the global small and medium-sized AMOLED panel industry, Korean manufacturers have accelerated their expansion with their technological advantages. In 2015, LG invested US$900 million to build a sixth-generation AMOLED production line with a monthly capacity of 7,500 substrates, equivalent to 15 million 5.5-inch screens. This production line is expected to be mass-produced in the first half of 2017. Samsung sold the LCD device in its L7 line and transformed it into an AMOLED line. And Samsung also plans to build a large-scale 8.5-generation AMOLED pilot line. The rest of the overseas panel makers also valued the investment opportunities of AMOLED, and some of them changed their original LCD production line into AMOLED production line, and some chose to build new AMOLED production line. Policy dividends help development, mainland manufacturers take advantage of the trend The Chinese mainland government has successively introduced relevant industry support policies. In the era of TFT-LCD display panels, due to the late start of China and the severe technical blockade from abroad, China's mainland has long been in an era of “lack of cores and less screensâ€. Nowadays, the third generation of display technology is rapidly emerging. The government of our country has continuously introduced relevant industry supporting policies and vigorously supported the development of China's AMOLED panel industry. The layout of domestic panel makers is accelerating, and it is predicted that the AMOLED production line will be fully produced in 2020. At present, China's AMOLED production line investment is in progress, and the number of AMOLED production lines that have been mass-produced is still very few. Most of the production lines are still in the stage of construction or capacity climbing. In the face of China's high-end domestic flagship mobile phones have thrown olive branches to AMOLED, but also suffer from the contradiction of insufficient supply in the market. Continental panel manufacturers continue to add AMOLED production line layout. Only eight production lines have started construction since 2016. It is expected that China's AMOLED production line will be fully operational in 2020. By then, the gap in the size of the AMOLED industry between China and South Korea will gradually narrow. The upstream of the industry is welcoming opportunities, and domestic substitution is just around the corner. The intensive investment in AMOLED production lines has brought strong market demand to the upstream of the industrial chain. At the current stage, the investment amount of a new AMOLED production line is equivalent to 1.5~2 times of the investment in the same capacity production line of TFT-LCD, of which equipment investment accounts for about 35.3%, and organic materials, glass and display chips account for 35.4%. That is to say, the cost of equipment and materials in the cost of AMOLED panels exceeds 70%, which indicates that the market space for upstream equipment and materials in the industry is broad and investment opportunities are considerable. The production enterprises in the upstream equipment field of the AMOLED industry chain have accumulated many years of mechanical industry and electrical automation technology, and have formed long-term and in-depth cooperation with panel companies, with strong technical barriers and market entry barriers. Equipment manufacturers that are currently able to provide capacity are mainly distributed in Japan, South Korea, and Taiwan, such as Tokki, Japan's Canon, Japan's SunicSystem, and Unitex. After years of digestive innovation and accumulation, relevant enterprises in mainland China have made key breakthroughs in the fields of detection signal types, detection system development, and detection technology. The gap between their technical level and international advanced manufacturers has been significantly reduced, and product prices have a comparative advantage. . At present, the trend of domestic replacement of AMOLED production line testing equipment appears, and it is expected to cut into the equipment supply chain of international manufacturers in the future. Continue to be optimistic about the upstream manufacturing equipment manufacturing enterprise of OLED production line: fine electronic measurement Jingzheng Electronics is China's leading supplier of flat panel display test systems. Its main products include module inspection system, panel inspection system, OLED inspection system, AOI optical inspection system and flat panel display automation equipment. In 2016, the company achieved a total operating income of 524 million yuan and a net profit of 99 million yuan. Among them, new products other than the module detection system and the panel inspection system contributed 52% of the revenue, and the performance drive was obvious. The company benefited from the trend of flat-panel display manufacturers' expansion and related equipment domestic substitution, and the assumption that the investment in the flat panel display market is proportional to the investment display equipment, the future industry is growing steadily. At the same time, through technology introduction and independent research and development, the company has achieved results and corresponding strategic layout in the three aspects of Module, AOI and OLED. The advantages of integration of light, machine and electricity have begun to take shape. Among them, Module strength is recognized by the industry and breaks through the automation direction; AOI's three major processes have heavy volume and move toward unmanned; OLED has achieved productization through LCD strength, and the next step will achieve commercialization goals.
There are many different versions of DIN Connectors. The name of each type comes from the number of pins the connector has (3-pin DIN, 4-pin DIN, etc.) Some of these pin numbers come in different configurations, with the pins arranged differently from one configuration to the next.
DIN cable connector 3-pin, 4-pin, 5-pin, 6-pin, 7-pin, 8-pin degree 180, 216, 240, 262, 270
DIN cables, DIN connector, telephone cable, computer cable, audio cable ETOP WIREHARNESS LIMITED , https://www.wireharness-assembling.com