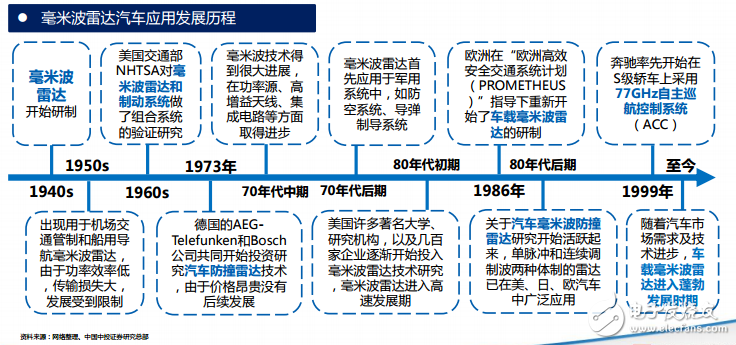
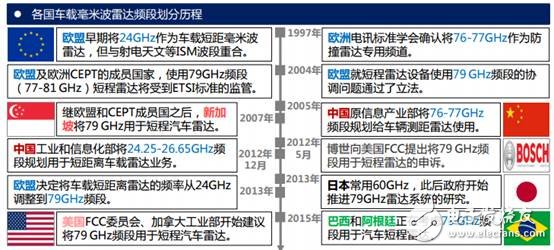
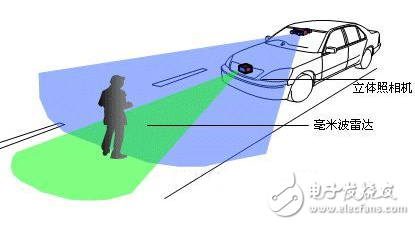
The millimeter wave radar will be the first to be the main sensor of the ADAS system due to its small size, easy integration and high spatial resolution. If you still don't know about millimeter wave radar and ADAS, please move to "ADAS is so popular, you still don't know about millimeter wave radar? 》 . After understanding the millimeter wave radar technology, its market status and market size will certainly attract your attention. Before talking about the size and status of the market, let us briefly understand the development of the millimeter wave radar. The research of vehicle-mounted millimeter-wave radar began in the 1960s, and the research was mainly carried out in developed countries such as Germany, the United States and Japan. The early on-board millimeter-wave radar developed slowly. After the 21st century, with the growth of the automotive market demand, it began to enter a booming period. In the development of millimeter wave radar, one problem that cannot be avoided is the frequency division of the vehicle millimeter wave radar. In order to avoid conflicts with other equipment bands, on-board radars need to allocate exclusive frequency bands, and the frequency bands are slightly different in each country. The 2015 World Radiocommunication Conference in Geneva allocated the 77.5-78.0 GHz band to the radiolocation service to support short-range high-resolution vehicles The development of radar, so that 76-81GHz can be used for on-board radar, the direction of the global vehicle millimeter wave radar unified direction. The advantage of the millimeter wave radar is that the angular resolution is high and the frequency bandwidth is favorable for the pulse compression technology, the Doppler shift, and the small size of the system. The disadvantage is that due to the large atmospheric absorption, the required transmission power and antenna gain are higher than those of the microwave system when a large working distance is required. According to the characteristics of millimeter wave radar, there are some typical application examples below. Car collision avoidance radar Since the distance of the action does not need to be very far, the output power of the transmitter does not need to be very high, but it requires a high range resolution (up to the meter level), and at the same time, the speed must be measured, and the volume of the radar should be as small as possible. Therefore, a millimeter-wave pulse Doppler radar using a solid-state oscillator as a transmitter is used. The pulse compression technique is used to compress the pulse width to the nanosecond level, which greatly improves the range resolution. Accurate velocity values ​​are obtained using the characteristics of millimeter-wave Doppler shifting. Space target recognition radar They are characterized by the use of large antennas to achieve the angular resolution required for imaging and high enough antenna gain, using high power transmitters to guarantee the range of action. For example, a space target recognition radar operating at 35 GHz has an antenna diameter of 36 m. Using a traveling wave tube to provide a transmission power of 10kw, it is possible to take pictures of satellites at a distance of 16,000km. An antenna target recognition radar operating at 94 GHz has an antenna diameter of 13.5 m. When the echo tube is used to provide 20kw of transmit power, high-resolution imaging can be performed on targets at a distance of 14,400km. Helicopter control radar In the crash of a modern helicopter, the accident caused by the collision of the aircraft with the high-voltage overhead cable accounted for a relatively high ratio. Therefore, the helicopter anti-control radar must be able to find high-voltage overhead cables with thin wire diameters. It is necessary to use short-wavelength radars with higher resolution, and actually use 3mm radar. Precision tracking radar The actual precision tracking radar is mostly a dual-frequency system, that is, one radar can work in the microwave frequency band (the distance is long and the tracking accuracy is poor) and the millimeter wave frequency band (the tracking accuracy is high and the working distance is short), and the two complement each other. Better results. For example, the dual-frequency precision tracking radar developed by the US Navy has a 9GHz, 300kw transmitter and a 35GHz, 13kw transmitter and corresponding receiving system. It shares a 2.4m parabolic antenna and has successfully tracked a height of 30m from the water surface. Target, the working distance can reach 27km. The double amount also brings an added benefit: the millimeter wave frequency can be used as a hidden frequency to improve the radar's anti-jamming capability. Pm Stepper Motor,Square Flange Stepper Motor,High Precision Stepper Motor,Permanent Magnet Stepper Motor Changzhou Sherry International Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.sherry-motor.com